Logistic-Regression 실습
분류 모델 실습
pima-indians-diabetes.csv 파일을 읽어서, 당뇨병을 분류하는 모델을 만드시오.
컬럼 정보 :
Preg=no. of pregnancy
Plas=Plasma
Pres=blood pressure
skin=skin thickness
test=insulin test
mass=body mass
pedi=diabetes pedigree function
age=age
class=target(diabetes of not, 1:diabetic, 0:not diabetic)
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sb
%matplotlib inline
import platform
from matplotlib import font_manager, rc
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
if platform.system() == 'Darwin':
rc('font', family='AppleGothic')
elif platform.system() == 'Windows':
path = "c:/Windows/Fonts/malgun.ttf"
font_name = font_manager.FontProperties(fname=path).get_name()
rc('font', family=font_name)
else:
print('Unknown system... sorry~~~~')
df = pd.read_csv('pima-indians-diabetes.csv')
df
| Preg | Plas | Pres | skin | test | mass | pedi | age | class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 | 148 | 72 | 35 | 0 | 33.6 | 0.627 | 50 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 85 | 66 | 29 | 0 | 26.6 | 0.351 | 31 | 0 |
| 2 | 8 | 183 | 64 | 0 | 0 | 23.3 | 0.672 | 32 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 89 | 66 | 23 | 94 | 28.1 | 0.167 | 21 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 137 | 40 | 35 | 168 | 43.1 | 2.288 | 33 | 1 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 763 | 10 | 101 | 76 | 48 | 180 | 32.9 | 0.171 | 63 | 0 |
| 764 | 2 | 122 | 70 | 27 | 0 | 36.8 | 0.340 | 27 | 0 |
| 765 | 5 | 121 | 72 | 23 | 112 | 26.2 | 0.245 | 30 | 0 |
| 766 | 1 | 126 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 30.1 | 0.349 | 47 | 1 |
| 767 | 1 | 93 | 70 | 31 | 0 | 30.4 | 0.315 | 23 | 0 |
768 rows × 9 columns
df.isna().sum()
Preg 0
Plas 0
Pres 0
skin 0
test 0
mass 0
pedi 0
age 0
class 0
dtype: int64
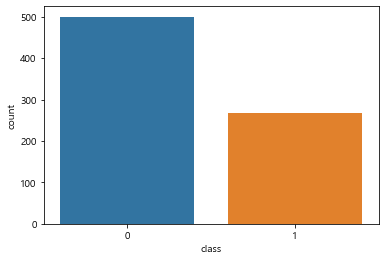
sb.countplot(data=df,x='class')
plt.show()
X = df.iloc[:,:8]
y= df['class']
# preg 컬럼은 0이 들어가도 된다.
# 이 컬럼을 제외한 나머지 컬럼들에 0이 있으면 모두 np.nan으로 변경
X.iloc[:,1:] = X.iloc[:,1:].replace(0,np.nan)
X.describe()
| Preg | Plas | Pres | skin | test | mass | pedi | age | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 768.000000 | 763.000000 | 733.000000 | 541.000000 | 394.000000 | 757.000000 | 768.000000 | 768.000000 |
| mean | 3.845052 | 121.686763 | 72.405184 | 29.153420 | 155.548223 | 32.457464 | 0.471876 | 33.240885 |
| std | 3.369578 | 30.535641 | 12.382158 | 10.476982 | 118.775855 | 6.924988 | 0.331329 | 11.760232 |
| min | 0.000000 | 44.000000 | 24.000000 | 7.000000 | 14.000000 | 18.200000 | 0.078000 | 21.000000 |
| 25% | 1.000000 | 99.000000 | 64.000000 | 22.000000 | 76.250000 | 27.500000 | 0.243750 | 24.000000 |
| 50% | 3.000000 | 117.000000 | 72.000000 | 29.000000 | 125.000000 | 32.300000 | 0.372500 | 29.000000 |
| 75% | 6.000000 | 141.000000 | 80.000000 | 36.000000 | 190.000000 | 36.600000 | 0.626250 | 41.000000 |
| max | 17.000000 | 199.000000 | 122.000000 | 99.000000 | 846.000000 | 67.100000 | 2.420000 | 81.000000 |
X.isna().sum()
Preg 0
Plas 5
Pres 35
skin 227
test 374
mass 11
pedi 0
age 0
dtype: int64
# 현재 X 와 y로 분리한 상태에서 0을 NaN으로 바꿨다.
# 따라서 Nan을 삭제할 경우! y 도 함께 처리해줘야 하는데, 어렵다.
# 그러므로 NaN 을 삭제하고 싶으면, X와 y 분리 전에 해줘야 한다.
# 이 예에서는, Nan을 각 컬럼의 평균값으로 채우는 전략을 사용한다.
X = X.fillna(X.mean())
X.isna().sum()
Preg 0
Plas 0
Pres 0
skin 0
test 0
mass 0
pedi 0
age 0
dtype: int64
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# 학습용 데이터와 테스트용 데이터.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.2,random_state= 10)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
classifier = LogisticRegression(random_state=10)
classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
LogisticRegression(random_state=10)
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
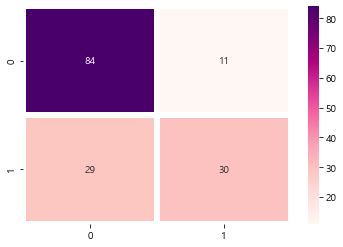
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm=confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred)
cm
array([[84, 11],
[29, 30]], dtype=int64)
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print(classification_report(y_test,y_pred))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.74 0.88 0.81 95
1 0.73 0.51 0.60 59
accuracy 0.74 154
macro avg 0.74 0.70 0.70 154
weighted avg 0.74 0.74 0.73 154
# 컨퓨전 메트릭스를, 히트맵으로 그려서 보기
sb.heatmap(data=cm,annot=True, cmap='RdPu',linewidths=5)
plt.show()
댓글남기기