머신러닝 - KNN
K-Nearest Neighbor
다음처럼 카테고리가 레이블링 되어 있는 데이터가 존재합니다.
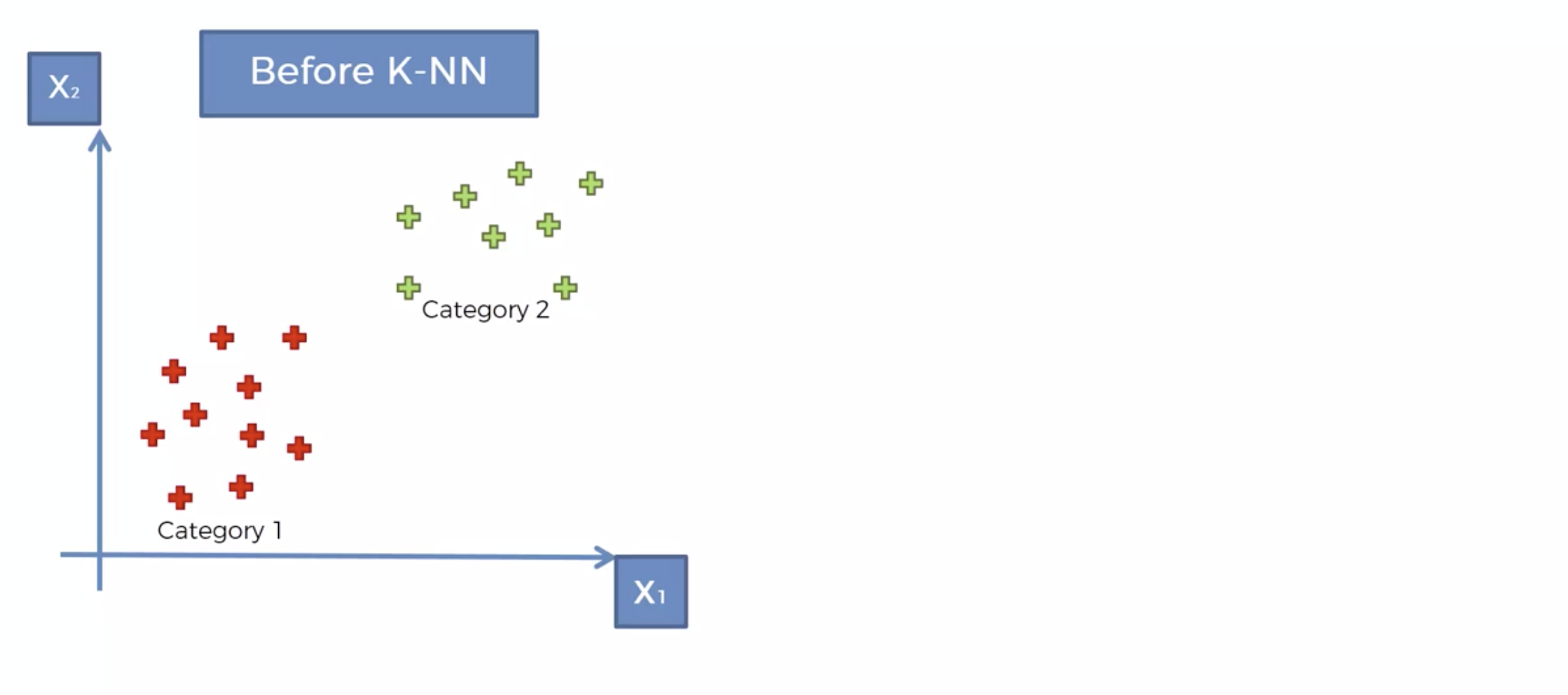
새로운 데이터가 생겼을때, 이를 어디로 분류해야 할까요?
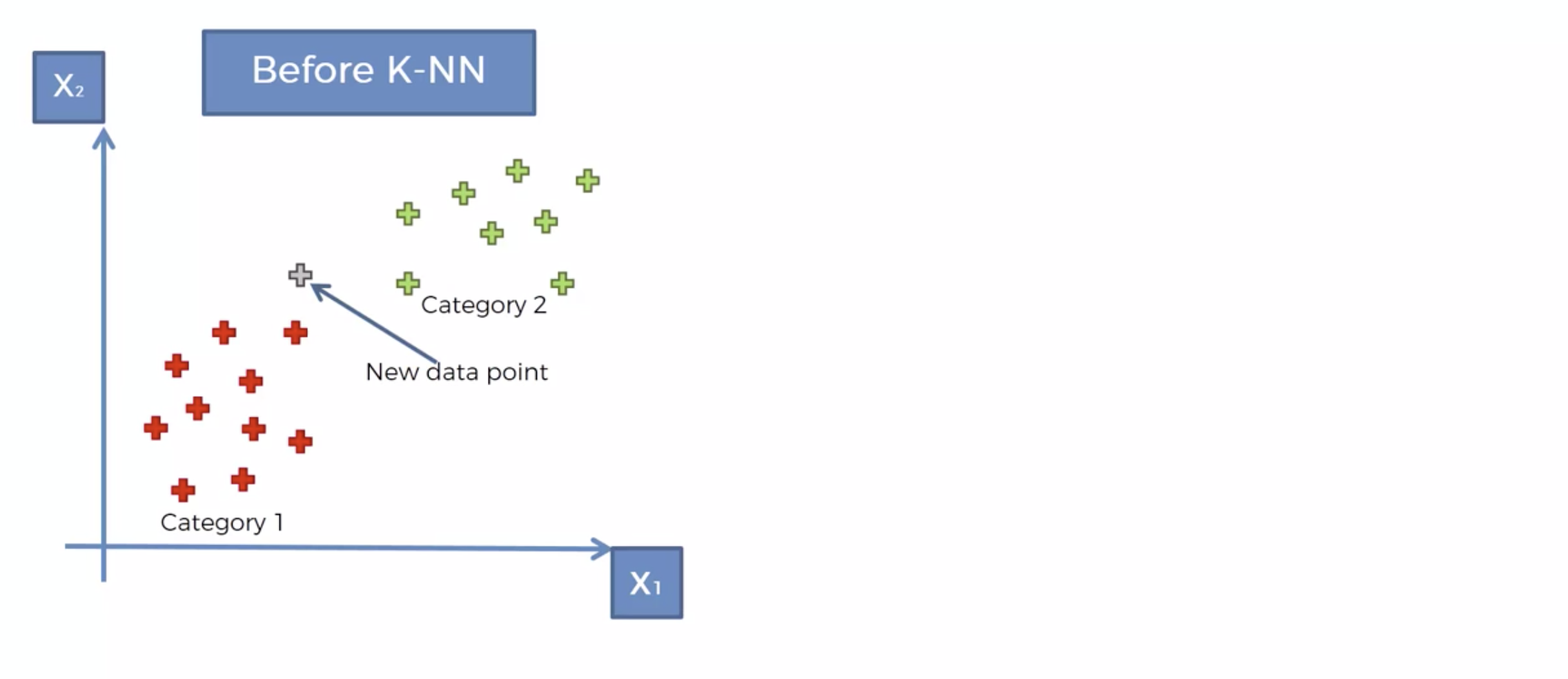
왜 빨간색으로 분류를 했을까요.
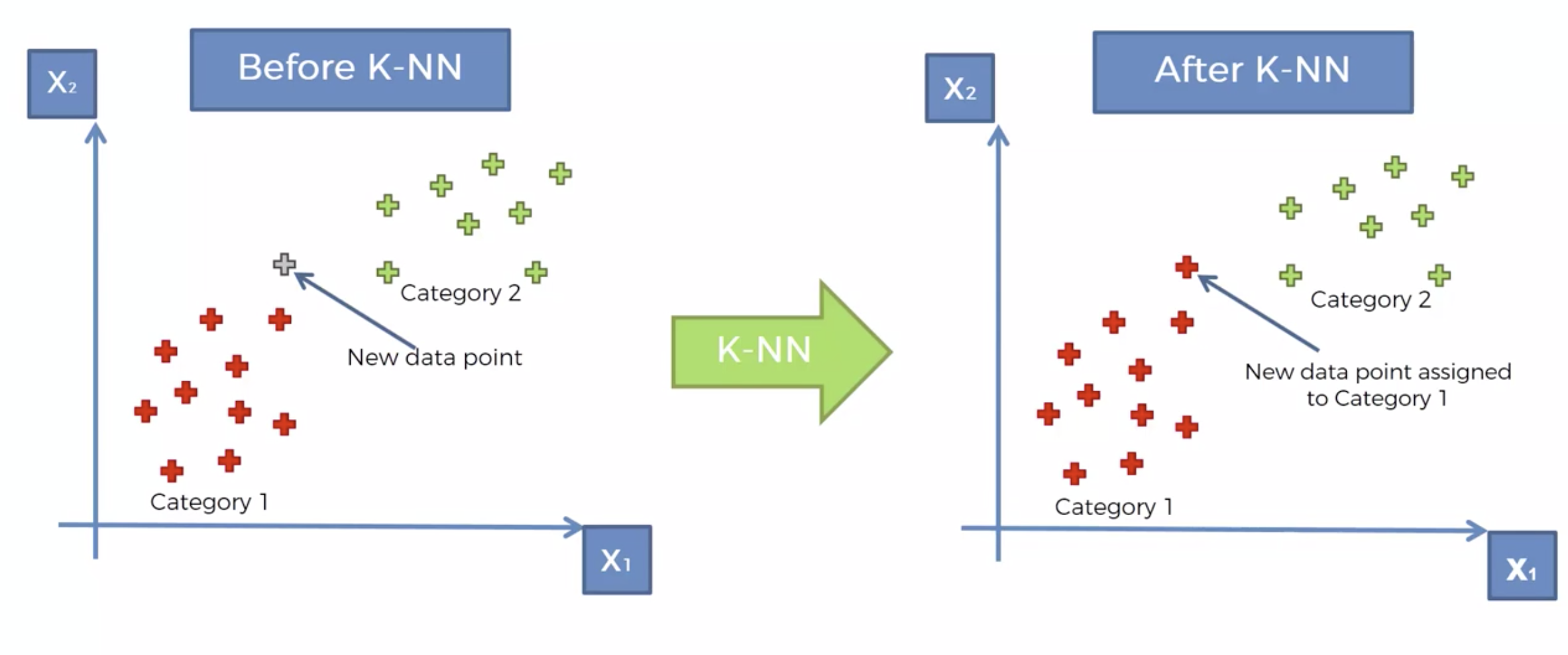
KNN 알고리즘
내 주위에 몇개의 이웃을 확인해 볼것인가를 결정한다. => K
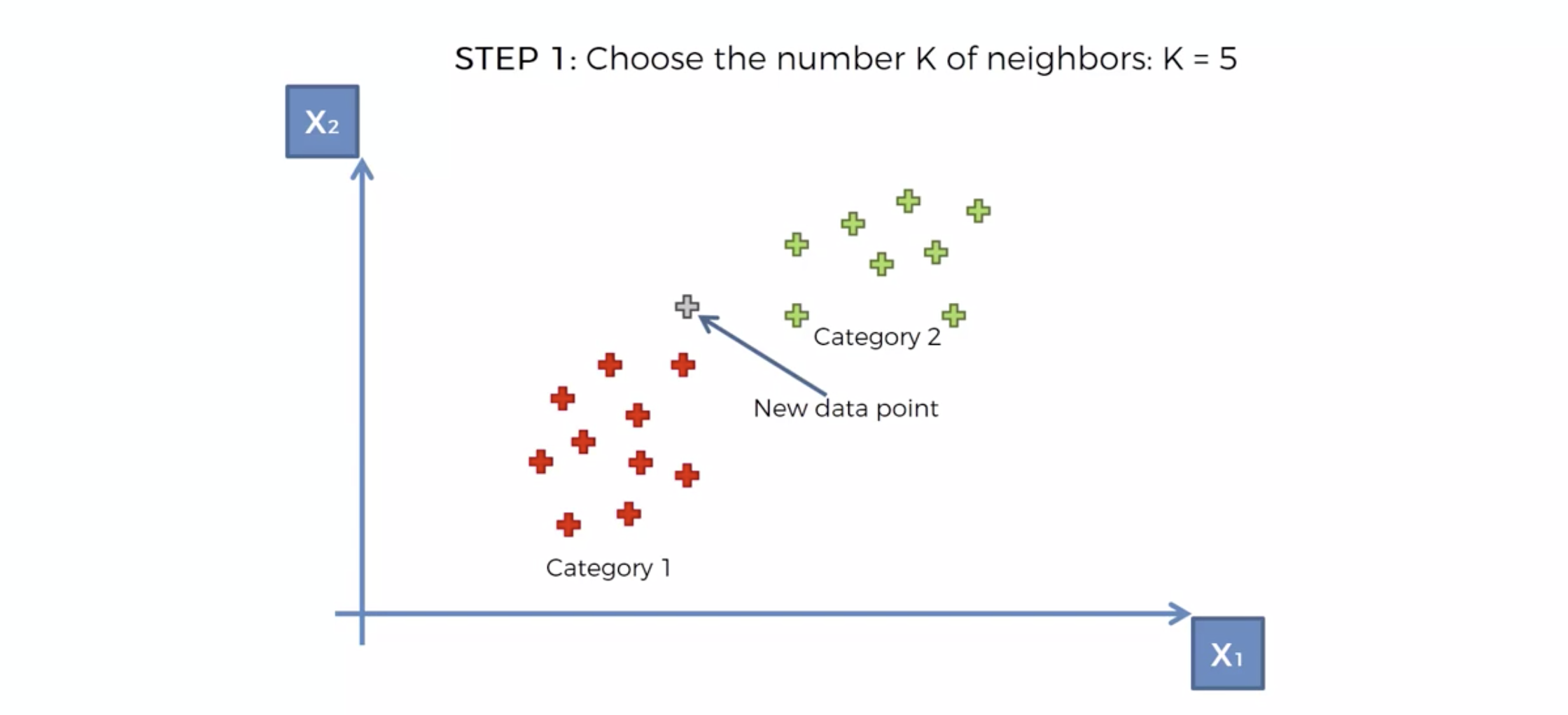
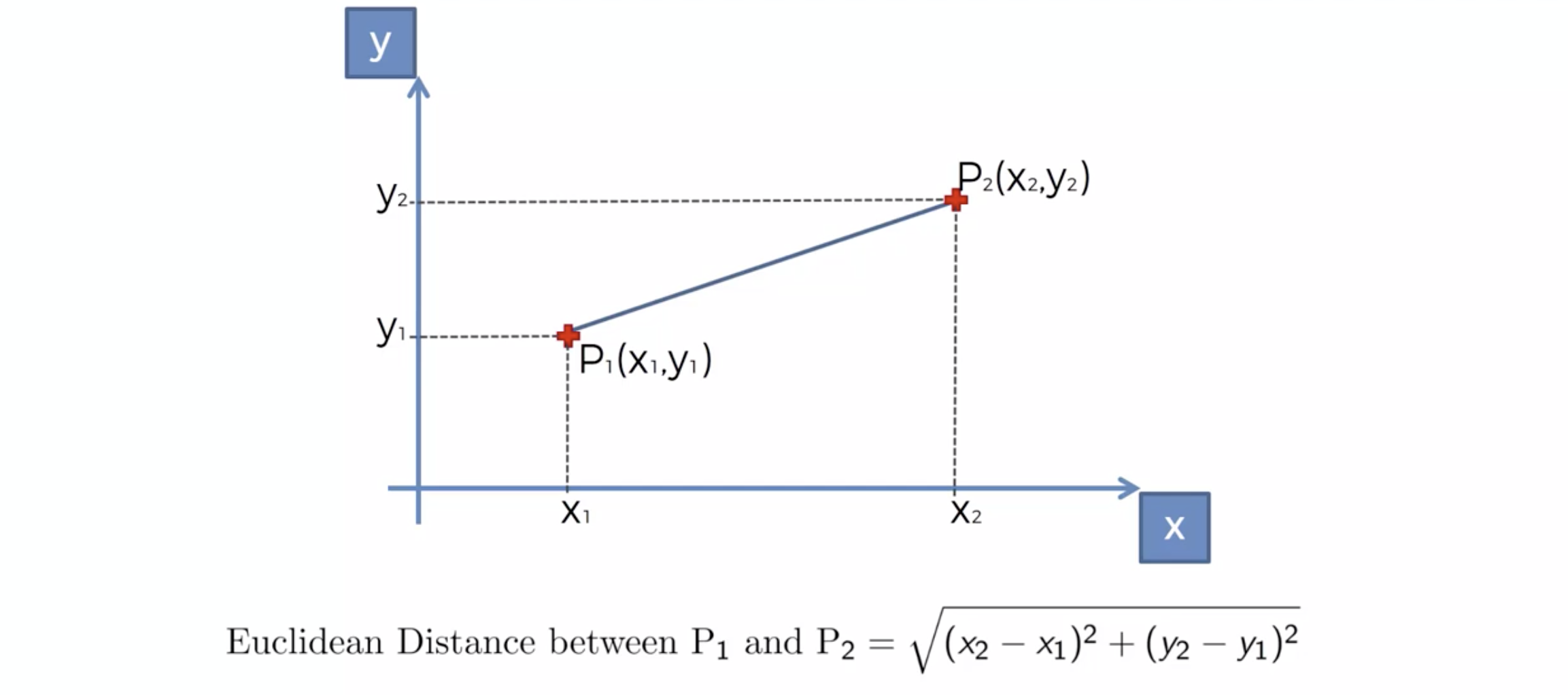
새로운 데이터가 발생 시, Euclidean distance 에 의해서, 가장 가까운 K 개의 이웃을 택한다.
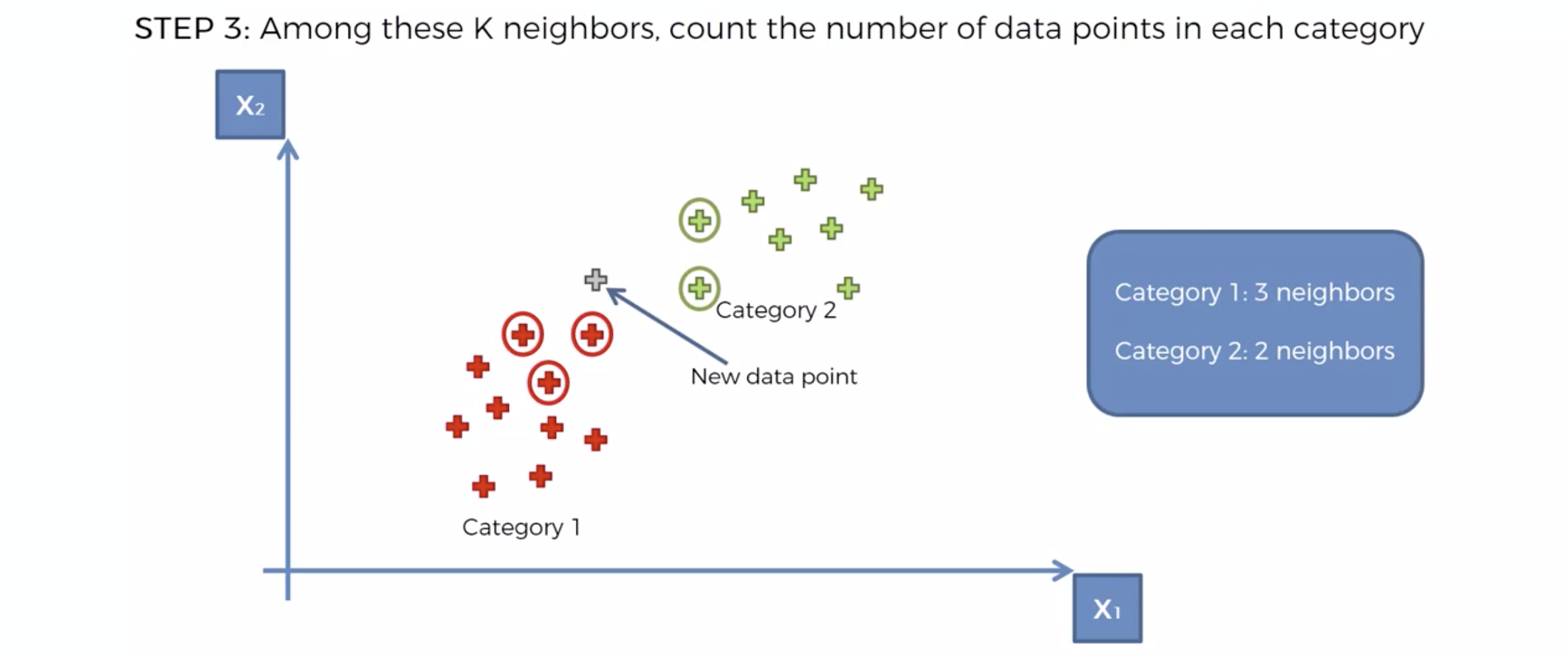
K 개의 이웃의 카테고리를 확인한다.
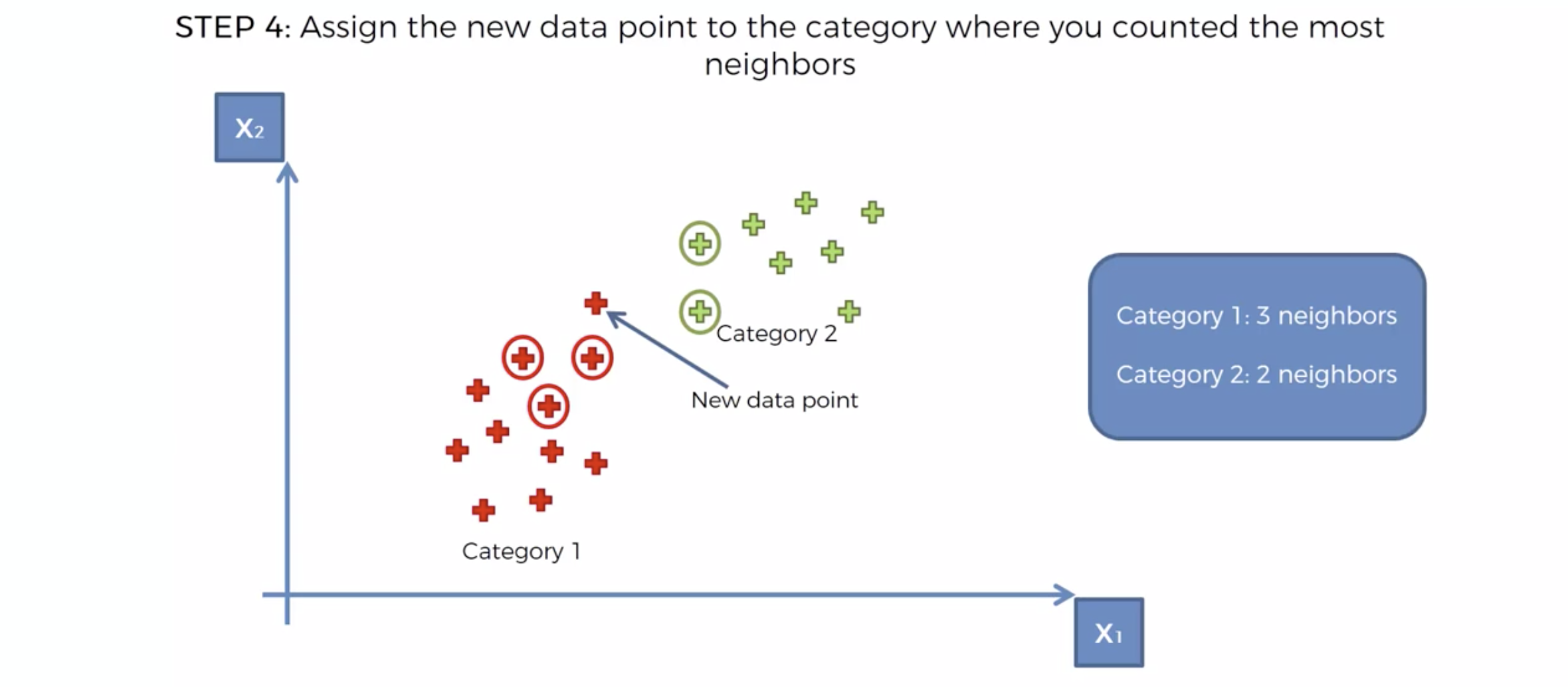
 카테고리의 숫자가 많은 쪽으로, 새로운 데이터의 카테고리를 정해버린다.
카테고리의 숫자가 많은 쪽으로, 새로운 데이터의 카테고리를 정해버린다.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sb
%matplotlib inline
import platform
from matplotlib import font_manager, rc
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
if platform.system() == 'Darwin':
rc('font', family='AppleGothic')
elif platform.system() == 'Windows':
path = "c:/Windows/Fonts/malgun.ttf"
font_name = font_manager.FontProperties(fname=path).get_name()
rc('font', family=font_name)
else:
print('Unknown system... sorry~~~~')
df = pd.read_csv('Social_Network_Ads.csv')
KNN 모델링
1. 데이터 분석
df.head()
| User ID | Gender | Age | EstimatedSalary | Purchased | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 15624510 | Male | 19 | 19000 | 0 |
| 1 | 15810944 | Male | 35 | 20000 | 0 |
| 2 | 15668575 | Female | 26 | 43000 | 0 |
| 3 | 15603246 | Female | 27 | 57000 | 0 |
| 4 | 15804002 | Male | 19 | 76000 | 0 |
2. 데이터 가공(피쳐 스케일링)
X = df.iloc[:,[2,3]]
y = df['Purchased']
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
3. 인공지능 학습
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.2,random_state= 3)
# KNN 으로 모델링
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
KNeighborsClassifier()
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
4. 인공지능 테스트
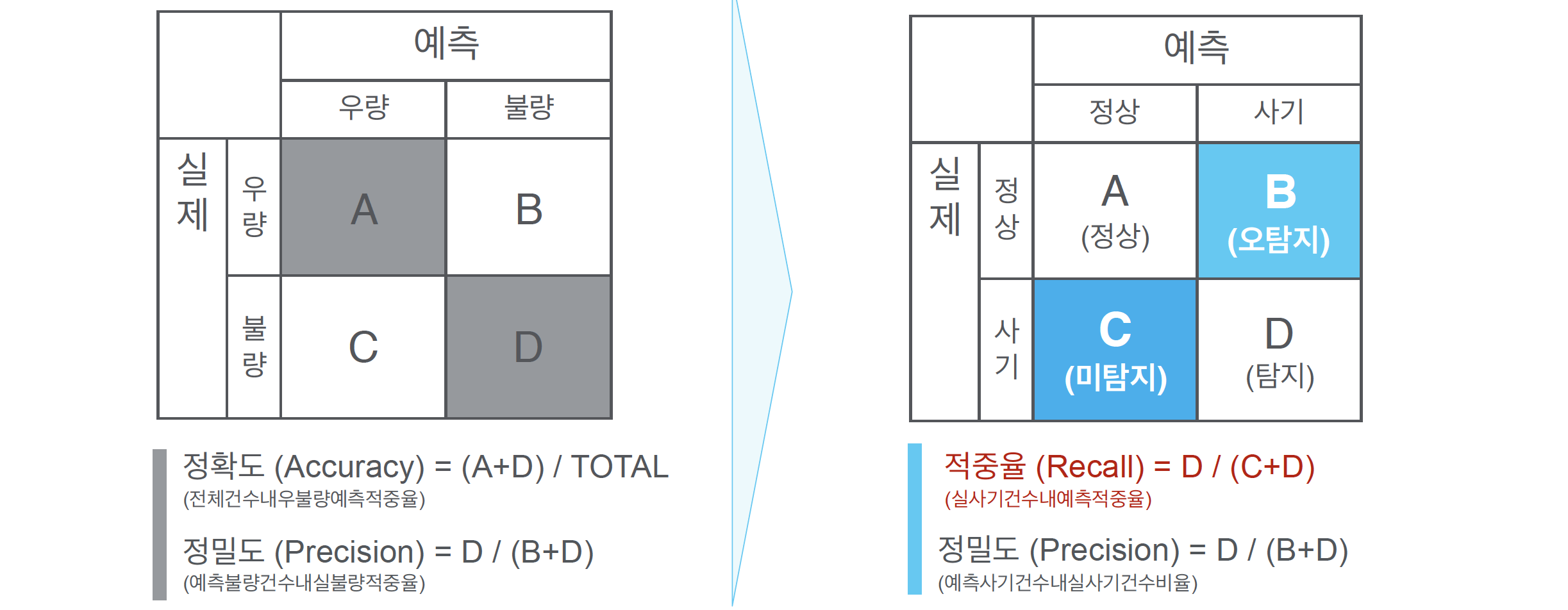
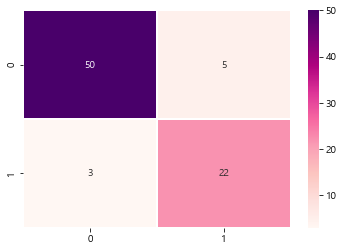
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred)
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print(classification_report(y_test,y_pred))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.94 0.91 0.93 55
1 0.81 0.88 0.85 25
accuracy 0.90 80
macro avg 0.88 0.89 0.89 80
weighted avg 0.90 0.90 0.90 80
sb.heatmap(data=cm,annot=True,cmap='RdPu',linewidths=0.5)
plt.show()
# Visualising the Test set results
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_test, y_test
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1,
stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1,
stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.figure(figsize=[10,7])
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(
np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
plt.title('Classifier (Test set)')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
*c* argument looks like a single numeric RGB or RGBA sequence, which should be avoided as value-mapping will have precedence in case its length matches with *x* & *y*. Please use the *color* keyword-argument or provide a 2-D array with a single row if you intend to specify the same RGB or RGBA value for all points.
*c* argument looks like a single numeric RGB or RGBA sequence, which should be avoided as value-mapping will have precedence in case its length matches with *x* & *y*. Please use the *color* keyword-argument or provide a 2-D array with a single row if you intend to specify the same RGB or RGBA value for all points.
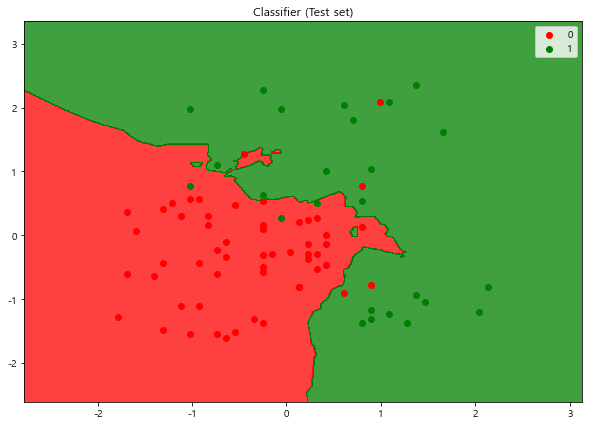
# 직선 : linear
# 직선이 아닌것들(지맘대로인것들) : non-linear
댓글남기기